How To Make Money With Treasury Bills
What are Treasury Bills (T-Bills)?
Treasury Bills (or T-Bills for short) are a short-term financial instrument that is issued by the US Treasury with maturity periods ranging from a few days up to 52 weeks (one year). They are considered among the safest investments since they are backed by the full religion and credit of the United States Government.
When an investor buys a Treasury Bill, they are lending money to the regime. The The states Government uses the money to fund its debt and pay ongoing expenses such as salaries and military equipment. T-Bills are sold in denominations ranging from $ane,000 (standard) up to a maximum of $5 million.
Example of Treasury Bills
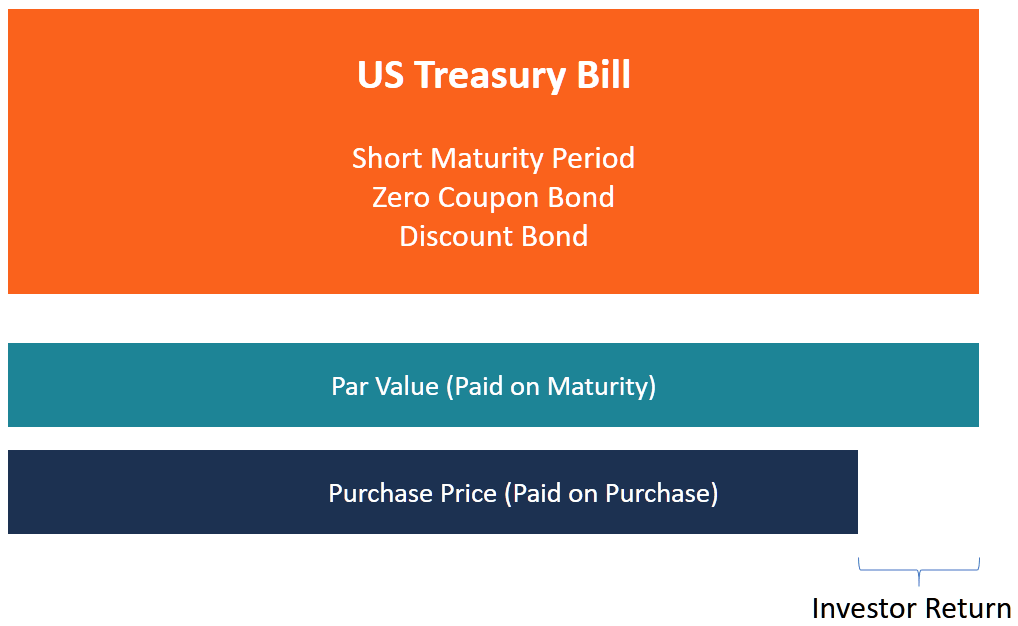
Treasury bills are sold at a disbelieve to the par value , which is its actual value. For example, a Treasury bill with a par value of $10,000 may be sold for $9,500. The Us Government, through the Section of Treasury, promises to pay the investor the total face value of the T-pecker at its specified maturity date.
Upon maturity, the government volition pay the investor $ten,000, resulting in a profit of $500. The amount of profit earned from the payment is considered the involvement earned on the T-pecker.
The departure betwixt the face up value of the T-pecker and the amount that an investor pays is called the discount rate, which is calculated every bit a percentage. In this case, the discount rate is 5% of the face value.
Become T-Bill rates directly from the US Treasury website.
How to Purchase Treasury Bills
Treasury bills tin can be purchased in the following three ways:
1. Not-competitive bid
In a not-competitive bid, the investor agrees to take the discount rate adamant at sale. The yield that an investor receives is equal to the boilerplate auction toll for T-bills sold at sale. Individual investors adopt this method since they are guaranteed to receive the full amount of the bill at the expiry of the maturity flow. Payment is made through TreasuryDirect or the investor's depository financial institution or broker.
ii. Competitive bidding auctions
In a competitive behest auction, investors buy T-bills at a specific discount rate that they are willing to accept. Every submitted bid states the everyman rate or discount margin that the applicant/investor is willing to accept. Bids accepting the lowest discount rate are accepted first.
If in that location are non enough bids at that level to brand the issue fully subscribed, then bids at the next lowest rate are accepted. The process continues until the entire issue has been sold. Purchase payments must be made either through a bank or a banker.
3. Secondary marketplace
Investors can purchase or sell Treasury bills on the secondary market place . Also, there are mutual funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) that agree previously issued T-bills.
Factors that Affect Treasury Nib Prices
Similar other types of debt securities, the price of T-bills and the return for investors may be affected by various factors such as macroeconomic conditions, investor risk tolerance, inflation, monetary policy, and specific supply and demand conditions for T-bills.
Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve'due south budgetary policy is probable to affect the T-bill price. T-bill involvement rates tend to move closer to the interest charge per unit ready by the Fed, known as the Fed(eral) Funds rate. Still, a rise in the Federal Funds rate tends to concenter investment in other debt securities, resulting in a drop in the T-bill interest charge per unit (due to lower demand). The reject continues until the T-pecker interest charge per unit rises above the Federal Funds rate.
Maturity Catamenia
The maturity menstruation of a T-bill affects its toll. For example, a one-year T-beak typically comes with a higher charge per unit of return than a three-month T-nib. The explanation for this is that longer maturities mean additional gamble for investors.
For example, a $ane,000 T-bill may be sold for $970 for a 3-calendar month T-nib, $950 for a six-month T-pecker, and $900 for a twelve-calendar month T-bill. Investors need a college charge per unit of return to compensate them for tying up their coin for a longer period of time.
Take a chance Tolerance
An investor'due south risk tolerance levels also touch the price of a T-beak. When the U.Southward. economy is going through an expansion and other debt securities are offering a higher return, T-bills are less attractive and will, therefore, be priced lower. Still, when the markets and the economy are volatile and other debt securities are considered riskier, T-bills command a higher price for their "safe haven" quality.
Inflation
The cost of T-bills can too exist afflicted by the prevailing charge per unit of inflation. For case, if the inflation rate stands at 5% and the T-neb discount rate is 3%, it becomes uneconomical to invest in T-bills since the existent rate of return will be a loss. The effect of this is that there is less demand for T-bills, and their prices will drib.
Departure between T-Bills, T-Notes, and T-Bonds
T-bills, T-notes, and T-bonds are fixed-income investments issued by the US Section of the Treasury when the government needs to borrow money. They are all commonly referred to as "Treasuries."
T-Bills
Treasury bills have a maturity of one year or less, and they do non pay interest before the expiry of the maturity menstruation. They are sold in auctions at a disbelieve from the par value of the pecker. They are offered with maturities of 28 days (1 month), 91 days (3 months), 182 days (vi months), and 364 days (one year).
T-Notes
Treasury notes have a maturity menstruation of two to ten years. They come in denominations of $ane,000 and offer coupon payments every half dozen months. The 10-year T-annotation is the about often quoted Treasury when assessing the performance of the bail marketplace. Information technology is besides used to show the marketplace's accept on macroeconomic expectations.
T-Bonds
Treasury bonds have the longest maturity among the iii Treasuries. They have a maturity menstruation of between 20 years and 30 years, with coupon payments every six months. T-bond offerings were suspended for four years between February 2002 and February 2006. T-bond offerings resumed due to need from pension funds and other long-term institutional investors.
More Resources
Thank you for reading CFI'south guide on Treasury Bills (T-Bills). To continue learning and advancing your career, these boosted resource will exist helpful:
- Debt Majuscule Markets
- Fixed Income Trading
- Bond Pricing
- Coupon Rate
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/trading-investing/treasury-bills-t-bills/
Posted by: covingtonfinand.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Make Money With Treasury Bills"
Post a Comment